Intro
This article analytically compares two major reference energy standards, ASHRAE 90.1 (2013) and NECB 2015, and spots the key differences between them. There are various parameters which are taken into account for this study such as climate zones, compliance path, HVAC systems, Schedules etc.
Climate Zones
The climate zones used for the article were selected by their number of Degree Days. ASHRAE utilizes both Heating and Cooling Degree-Day categories to classify their climate zones. NECB 2015, however, utilizes only Heating Degree-Days for its categorization. Also, ASHRAE identifies HDD 5000 to 7000 as zone 7 whereas NECB further classifies them into zones named 7A (HDD 5000 to 6000) and 7B (HDD 6000 to 7000), as seen below.
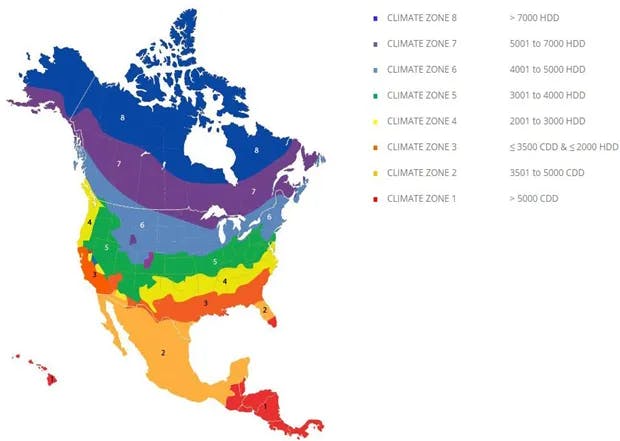
[1] Figure 1 ASHRAE Climate Zones
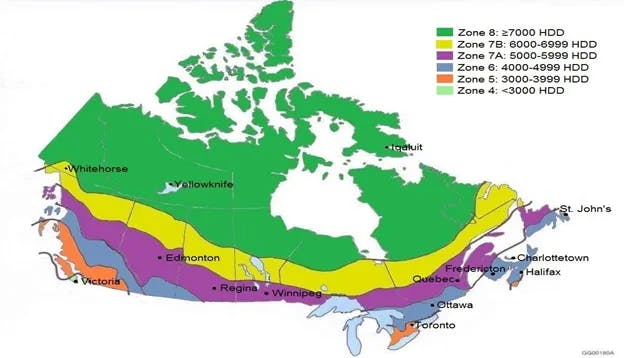
[2] Figure 2 Canada NECB Climate Zone
Compliance Path
ASHRAE 90.1 (2013) and NECB 2015 both have similarly structured compliance paths. The principal difference is that ASHRAE has additional mandatory requirements for any path chosen whereas for NECB almost all requirements are prescriptive. Also, with NECB there are trade-off paths that one can pursue to achieve compliance.
HAVC Systems
For baseline system modeling, ASHRAE suggests that each HVAC system in a proposed building design should be matched on a one-to-one correspondence with one of the 13 HVAC systems in Table G3.1.1-4. NECB, on the other hand, suggests selecting a system based on your space type listed in table 8.4.4.7.-A. The definitions for 7 different systems are given in table 8.4.4.7.-B. If the proposed space type is not present in the table 8.4.4.7.-A then the system which most closely corresponds to that system should be selected.
Lighting and Plug Loads
The lighting loads for ASHRAE 90.1 and NECB standard building types are similar across the board. However, the Plug loads for ASHRAE 2013 User Manual and NECB 2015 are different for the categories shown here:
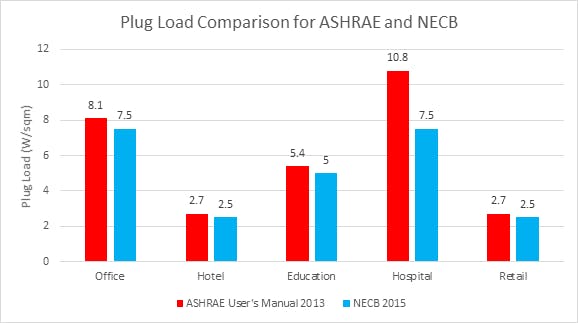
Figure 3 Plug Load comparison for ASHRAE and NECB
Occupancy
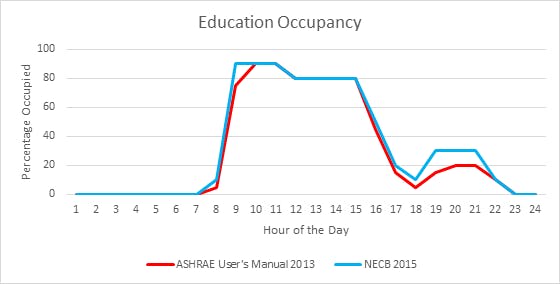
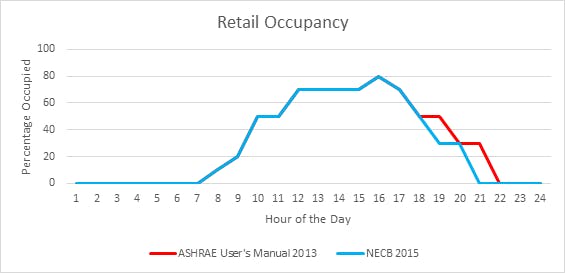
The occupancy schedules used for ASHRAE and NECB also differ in a couple categories as shown in the graphs below:
I. Office
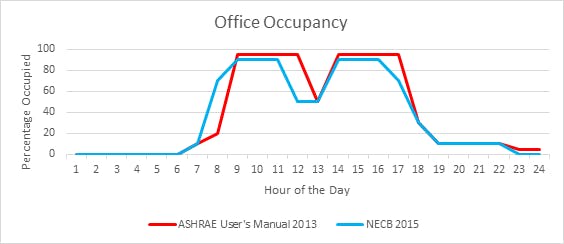
II. Education
III. Retail
Observation and Conclusions
- ASHRAE 90.1 mainly considers energy cost and NECB considers energy consumption to achieve compliance.
- NECB has stricter policies for a building’s thermal envelope than ASHRAE 90.1.
- After running the models in cove.tool for ASHRAE zone 6 (Helena, MT) and NECB zone 6 (Ottawa, ON), minimum compliance for NECB 2015 results in lower energy use than ASHRAE 90.1 2013 as shown in attached graphs.
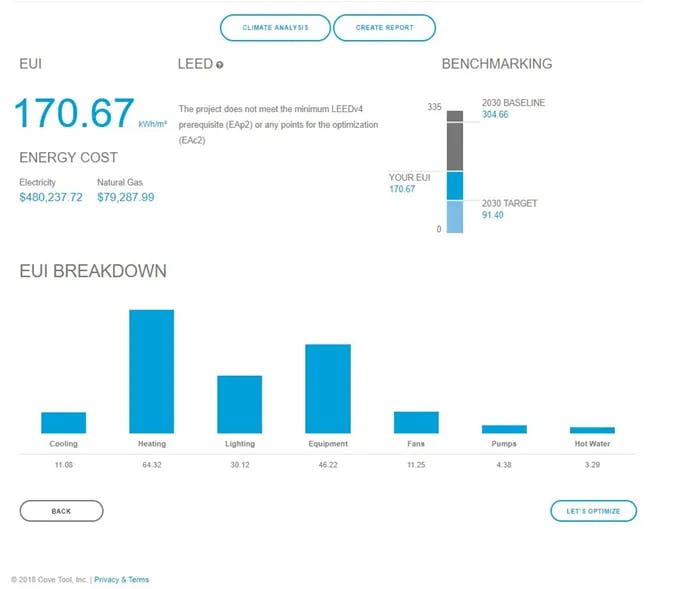
Figure 4 Large Office at Helena, MT with ASHRAE 2013 Inputs
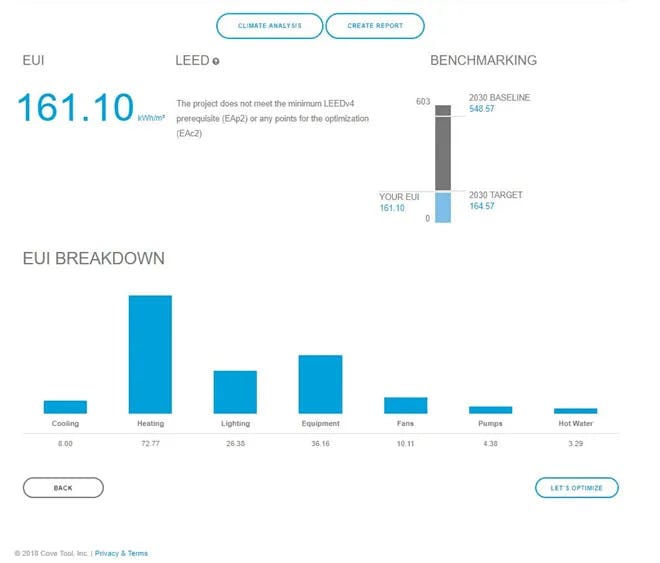
Figure 5 Large Office at Ottowa, ON with NECB 2015 Inputs
Reference
[1]. ASHRAE Climate Zones by Akira Living.
[2]. NECB climate zones by NAIMA Canada.
[3]. https://www.canadianconsultingengineer.com/features/which-to-choose-ashrae-90-1-2010-or-necb-2011/
[4]. https://www.bicsi.org/docs/default-source/conference-presentations/2017-canada/green-building-metrics-codes-standards.pdf?sfvrsn=75e3d6b_2
