Introduction to Ground Source Heat Pumps
An innovative technology called Ground Source Heat Pumps (GSHPs) utilize the earth's natural heat to provide heating and cooling for buildings. GSHPs are quickly gaining popularity, especially in areas with extreme temperatures, as an energy-efficient, environmentally friendly, and sustainable alternative to conventional heating and cooling methods.
Efficiency and Flexibility
One of the most significant advantages of adopting GSHPs over traditional fossil fuel-burning boilers, furnaces, or electric resistance heaters is their efficiency. Since GSHPs make use of the earth's inherent heat, they use less energy to run, which can significantly reduce energy costs. GSHPs are a flexible solution for year-round comfort since they can be utilized for both heating and cooling. Residential, commercial, and industrial applications of this technology are all possible for installation in different kinds of buildings.
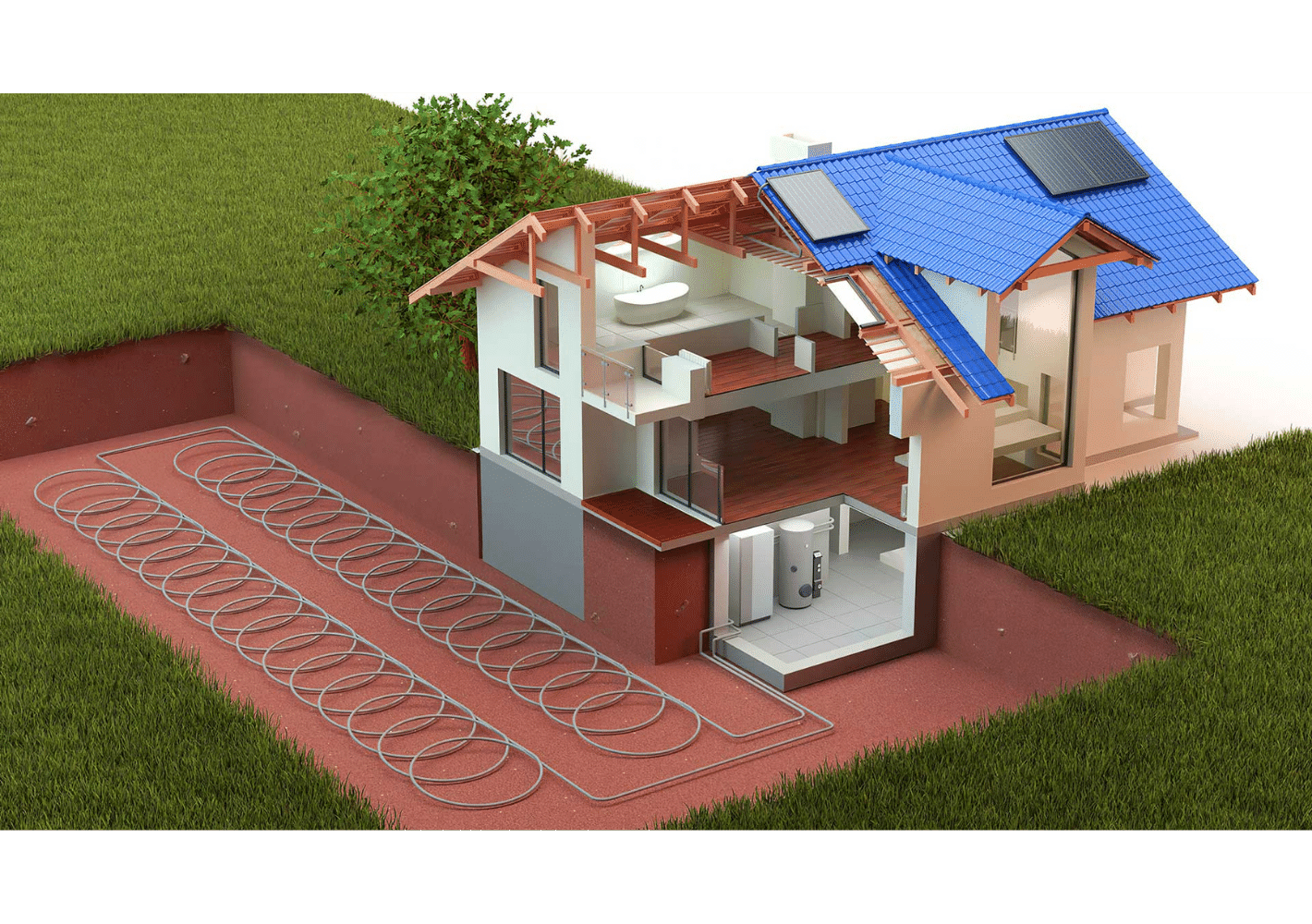
Source: Lipford, D. (2023, February 2). Geothermal Heat Pumps Offer Comfort and Efficiency. Today’s Homeowner. https://todayshomeowner.com/hvac/guides/whats-the-best-way-to-heat-and-cool-a-home-efficiently/
Operation and Installation
GSHPs operate by pumping fluid through an underground, closed-loop network of pipes. During the winter, the fluid pulls heat from the soil and transports it to the building providing heat. During the summer, on the other hand, the fluid removes heat from the structure and returns it to the earth for cooling. In order to construct a GSHP, the building's heating and cooling needs must be taken into consideration while choosing an acceptable site for the underground pipes and the system size required.
Importance of Building Insulation
For a GSHP system to operate at its best efficiency and effectiveness, a building must be well-insulated. Insufficient insulation can make a system less efficient and effective, which raises energy costs. The cost of installation must also be taken into account. However, analysis will show that first cost of a larger GSHP system will be higher than the insulation. GSHPs have the potential to save money over the long run, but they can be expensive to install initially. Therefore, a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis is crucial to determining if this technology is feasible.
The advantages of GSHPs for the environment are also substantial. Because they employ only electricity, they have the potential to use only renewable energy, leading to fewer greenhouse gases (GHGs) emissions than conventional systems. They are, therefore, a sustainable and responsible choice for building owners because they may aid in lowering carbon footprints.
Building Types and Requirements
GSHPs are an excellent choice for a variety of building types, including schools, hospitals, and industrial buildings. They may also be tailored to suit a wide range of heating and cooling requirements. The adaptability of GSHPs is particularly helpful in commercial and industrial settings where continuous, high-demand heating and cooling is necessary. As a green way to regulate the temperature of buildings, GSHPs are gaining popularity. Compared to traditional techniques, they provide several advantages, including space saving inside the building, lower energy use, lower carbon emissions, and longer-term cost savings. However, there are a number of important things to think about before setting up a GSHP system.
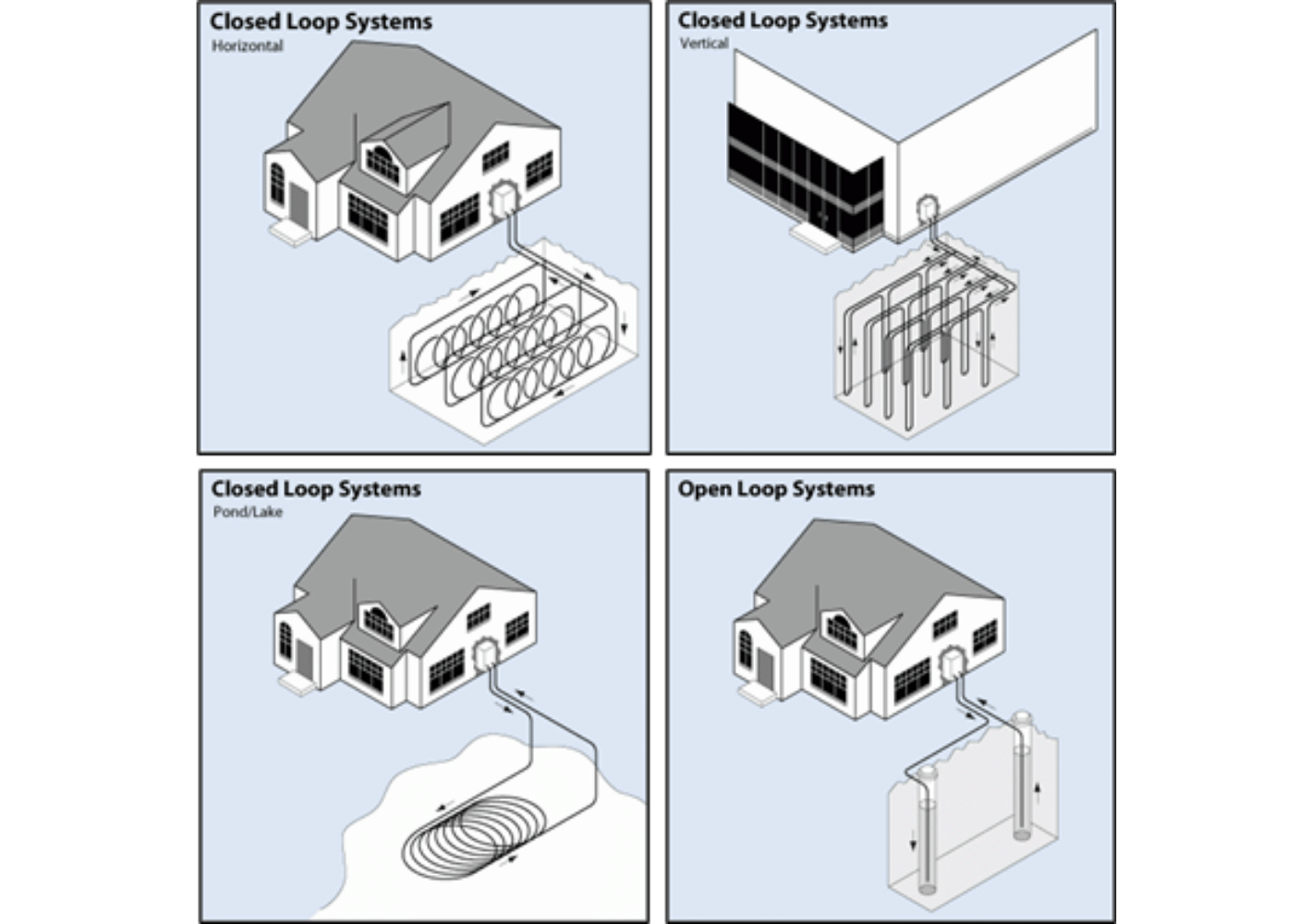
Source: Geothermal Heat Pumps. (n.d.). Energy.gov. https://www.energy.gov/energysaver/geothermal-heat-pumps
System Design and Placement
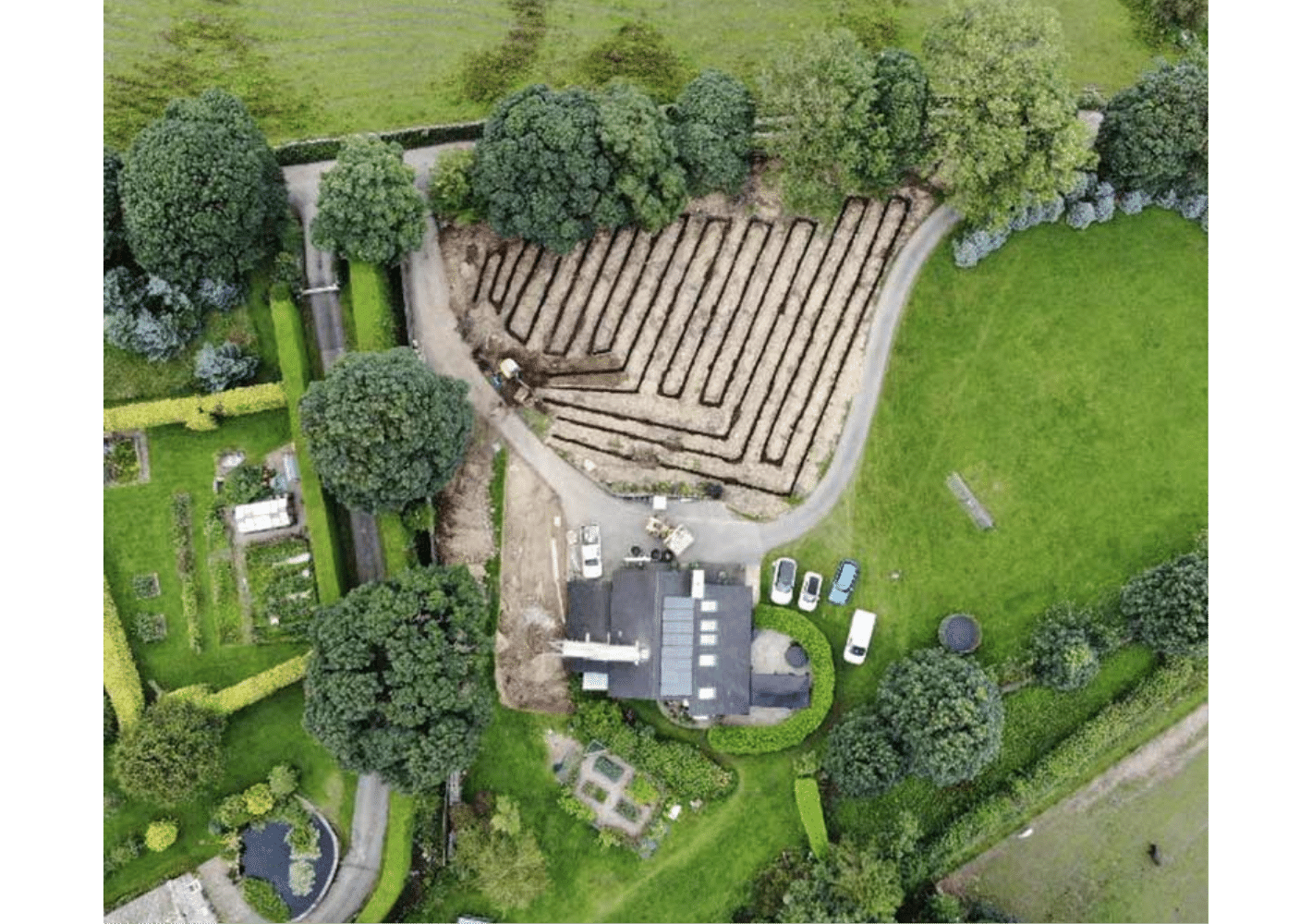
The system's design presents an important consideration. There are several types of GSHP systems, including closed-loop and open-loop systems. Between the heat pump and the ground heat exchanger, closed-loop systems circulate a refrigerant. In open-loop systems, groundwater is immediately pumped from a well to the heat pump. The system's design is influenced by a number of variables, such as ground and surface water quality, rock and soil forms, and installation costs. Another important consideration is placement. Ground conditions, building orientation, and space availability are only a few examples of the variables that affect the placement. Because of its installation location, the ground heat exchanger should be able to extract or reject heat to the ground effectively. Poor system placement can lead to decreased performance, greater energy expenditures, and more expensive installation.
Another crucial aspect to take into account when installing a GSHP system is building insulation. Lack of insulation may cause heat to escape, which will make the GSHP system work harder and less effectively. Spray foam, fiberglass, and cellulose are a few insulation materials that can help lower heat loss, increase energy efficiency, and lessen the heating and cooling load on the GSHP system.
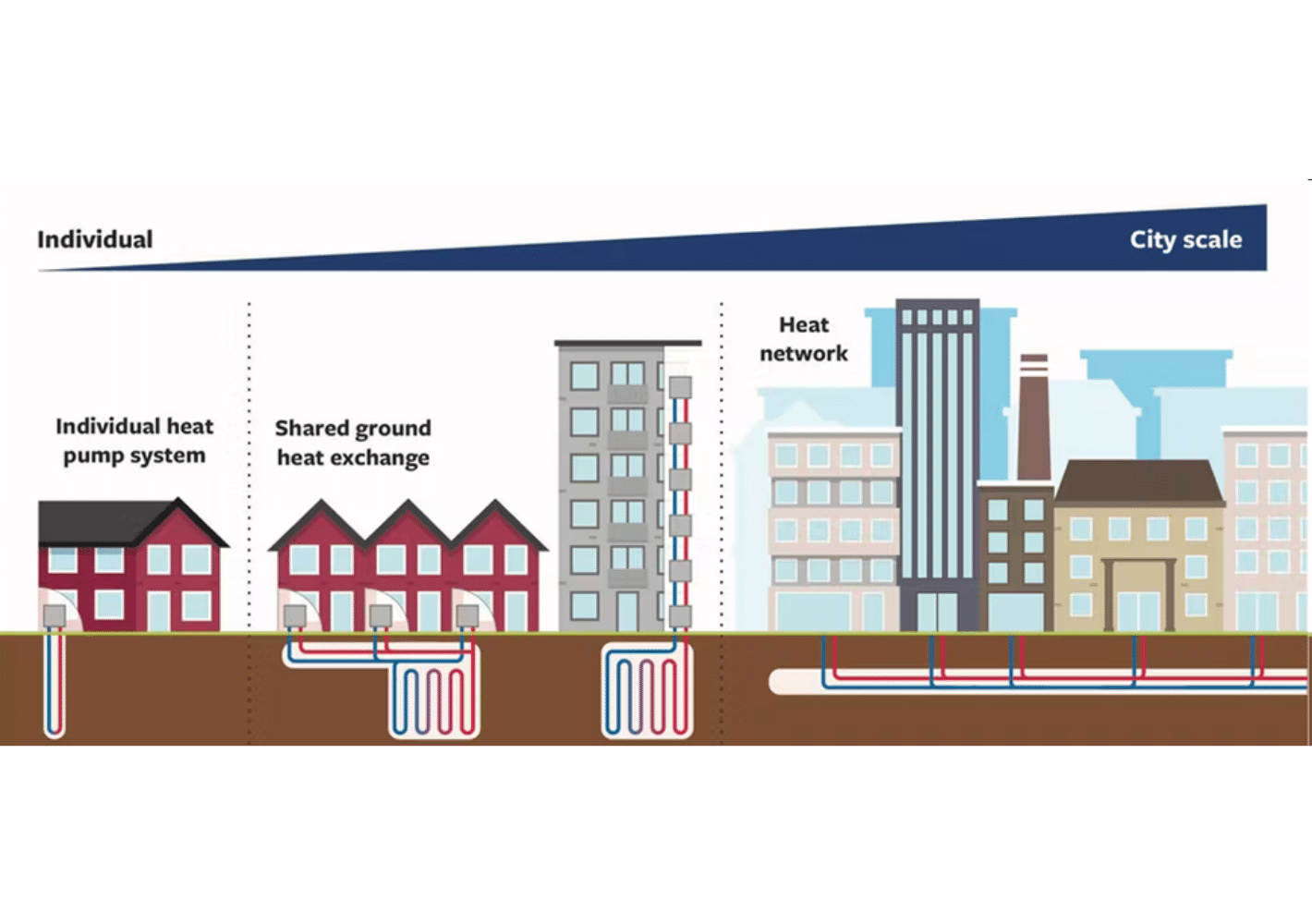
Source: Barns, D. (2022, May 10). How a street can share a Ground Source Heat Pump - Energy Post. Energy Post. https://energypost.eu/how-a-street-can-share-a-ground-source-heat-pump/
When planning to replace or update an HVAC system, system size is another significant factor to take into account. The building's heating and cooling needs, which can change based on a number of variables, including the building's size, occupancy, location, and orientation, dictate the size of the system. In addition to maximizing comfort and efficiency, a correctly designed GSHP system must also be balanced to ensure the longevity of the system.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Cost-benefit analysis is particularly crucial when thinking about installing a GSHP system. GSHP systems may result in long-term cost reductions, but they may also have a high initial cost. The system's complexity, size, location, and cost of personnel and materials are some of the variables that affect installation costs. For the purpose of determining whether an investment in a GSHP system is financially feasible, a cost-benefit analysis should consider the initial installation costs, continuing maintenance and repair expenses, and long-term energy savings. When establishing a GSHP system, there are various regulatory requirements in addition to financial ones to take into account. For the construction and operation of a GSHP system, permits and inspections may be necessary depending on the location's building laws and regulations. To prevent any fines or other penalties, building owners should make sure they adhere to all applicable laws and regulations.
GSHPs and loadmodeling.tool
In loadmodeling.tool, GSHP can be configured on the Mechanical Plants page. A fully defined system is divided into three main plant loops.
First, the condenser loop represents the ground heat exchanger as a series of bore holes. Details about the pipework and ground such as the ground thermal conductivity, pipe diameter, and depth are captured here. Next, the configuration of the heat pump portion of the GSHP is defined for both cooling and heating modes of operation. This connects the GSHP into the equipment delivering heating and cooling to the building such as air handling units, radiant panels and more. By simulating the GSHP system on loadmodeling.tool engineers can see annual energy consumption and cost needed to perform the cost-benefit analysis. Additionally, the hourly heat and cooling loads for the building can be reported and shared with the geotechnical consultant. This is a critical step that ensures the system is well balanced, leading to optimum performance over the life of the equipment.

Source: All Seasons Energy. (2022, December 6). Ground Source Heat Pumps | GSHP Installers | All Seasons Energy. https://allseasonsenergy.co.uk/heat-pumps/ground-source-heat-pumps/
Considerations for GSHPs
GSHP systems are an innovative and sustainable technology that provides various advantages compared to conventional heating and cooling methods. They can lead to long-term cost savings as well as decreased energy consumption and carbon emissions.
Before installing a GSHP system, there are a number of important elements to take into account, including the system's design, location, insulation, size, and cost-benefit analysis. To prevent any fines or other consequences, building owners should also make sure that all applicable laws and regulations are followed. With careful thought and preparation, GSHP systems may offer optimal efficiency and comfort for many years.
